Electricity Planning Model (EPM)
Bosnia and Herzegovina
Botswana
Burkina Faso
Chad
Djibouti
Egypt
Gambia
Georgia
Iraq
Lao (PDR)
Liberia
Maldives
Mauritania
Morocco
Namibia
Nigeria
Poland
Rwanda
Sao Tome and Principe
Senegal
Sierra Leone
Sudan
Ukraine
About epm
EPM (Electricity Planning Model) is a least-cost power system planning tool. EPM has been developed by the Power Systems Planning Group, embedded in the Energy Sector Management Assistance Program (ESMAP) of the World Bank. As power system planning is one of the key activities performed by energy ministries and utilities around the world, the ambition of this tool is to actively inform the operational work of the World Bank's staff and clients and to be an evolving and versatile decision-making tool.
EPM is formulated in the General Algebraic Modeling System (GAMS). All input data is provided via an Excel interface to the model and likewise, the results are collected in an Excel output file. Knowledge of the GAMS programming language is not a prerequisite for the basic runs. In short, EPM minimizes the costs of expanding and operating a power system while meeting the system's technical, economic, and environmental requirements. EPM is mostly used as a long-term planning model, which means it optimizes the capacity expansion on a yearly basis based on system costs over multiple years, including fixed costs (annualized capital and fixed operation and maintenance [O&M]), variable costs (variable O&M) and fuel costs. Moreover, EPM addresses the dispatch of the generators, decides on the activities per geographical zone and the exchange between them. The model also co-optimizes reserves and generation allowing to allocate spinning reserves among generators. It also allows to test the impact of different policies, e.g., emissions limits, fuel, and import limits, spinning reserve requirements, transmissions caps, ramp limits, or carbon prices, on the power system evolution and costs.
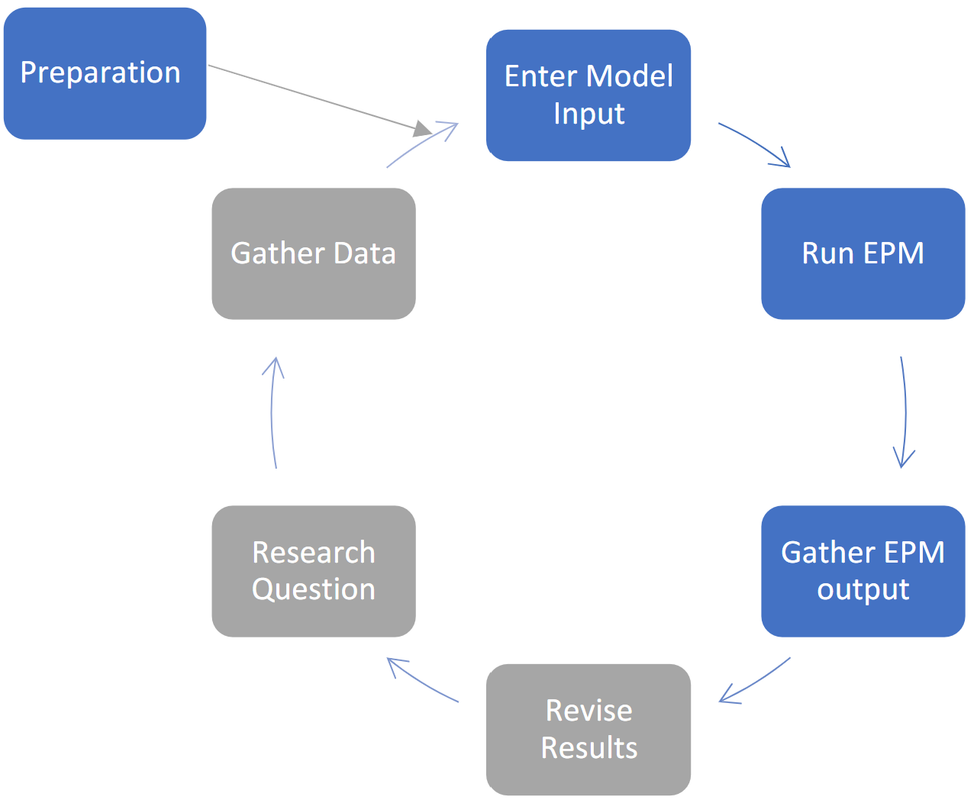
The practical deployment of EPM consists of a 7-step process, which is illustrated here.